The Honeywell HMC5983 is a temperature compensated three-axis integrated circuit magnetometer. This surface-mount, multi-chip module is designed for low-field magnetic sensing for applications such as automotive and personal navigation, vehicle detection, and pointing. The HMC5983 includes our state-of-the-art, high-resolution HMC118X series magnetoresistive sensors plus an ASIC containing amplification, automatic degaussing strap drivers, offset cancellation, and a 12-bit ADC that enables 1° to 2° compass heading accuracy.
The I²C or SPI serial bus allows for easy interface. The HMC5983 utilizes Honeywell’s Anisotropic Magnetoresistive (AMR) technology that provides advantages over other magnetic sensor technologies. Honeywell’s anisotropic, directional sensors excel in linearity, low hysteresis, null output and scale factor stability over temperature, and with very low cross-axis sensitivity. These sensors’ solid-state construction is designed to measure both the direction and the magnitude of magnetic fields, from milli-gauss to 8 gauss. Honeywell’s Magnetic Sensors are among the most sensitive and reliable low-field sensors in the industry
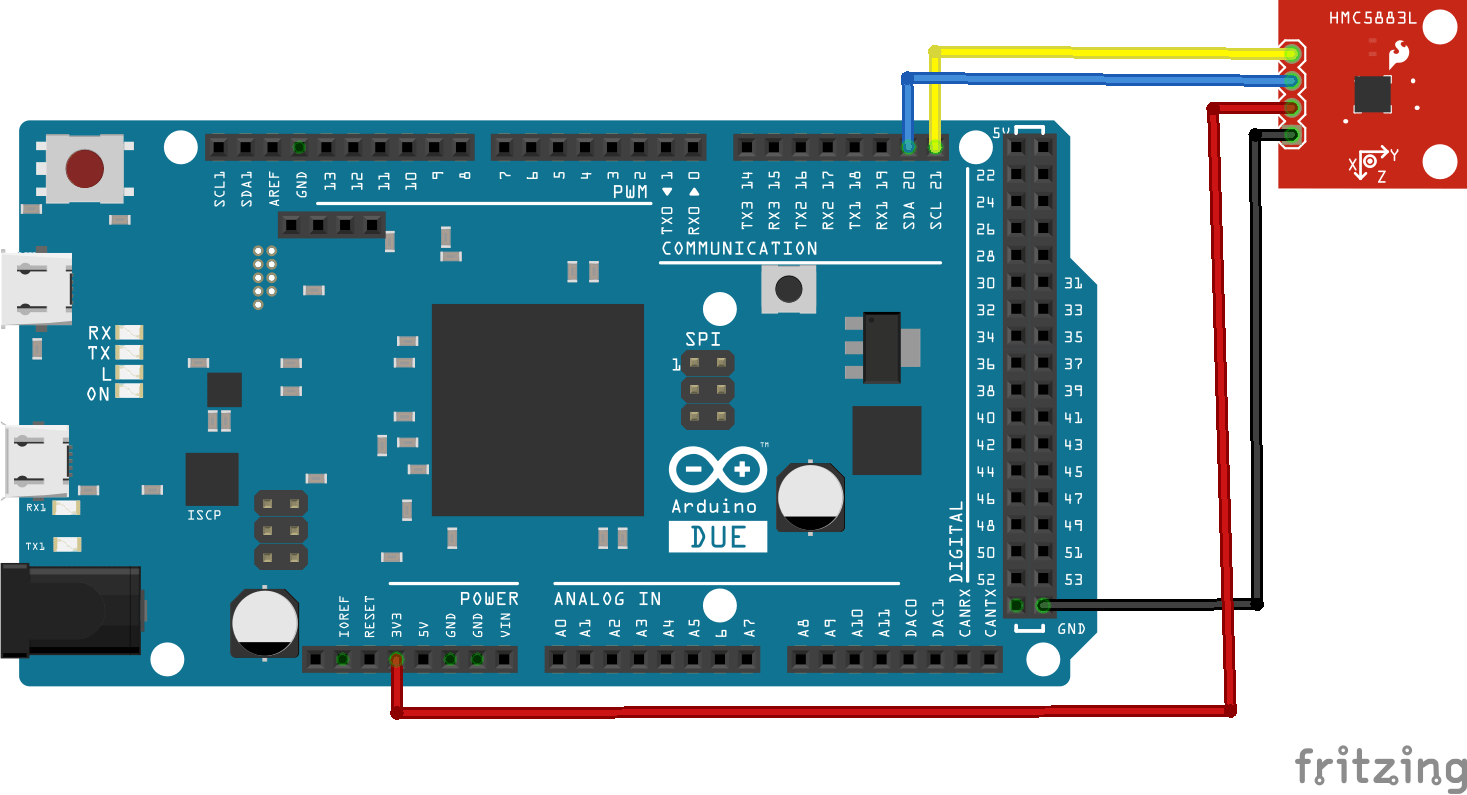
Schematic
The layout example shows a 5883L but the 5983L has exactly the same connection
Code
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h> //I2C Arduino Library
#define addr 0x1E //I2C Address for The HMC5983
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
Wire.beginTransmission(addr); //start talking
Wire.write(0x02); // Set the Register
Wire.write(0x00); // Tell the HMC5883 to Continuously Measure
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void loop()
{
int x,y,z;
//Tell the HMC what regist to begin writing data into
Wire.beginTransmission(addr);
Wire.write(0x03);
Wire.endTransmission();
//Read the data
Wire.requestFrom(addr, 6);
if(6<=Wire.available())
{
x = Wire.read()<<8; //MSB x
x |= Wire.read(); //LSB x
z = Wire.read()<<8; //MSB z
z |= Wire.read(); //LSB z
y = Wire.read()<<8; //MSB y
y |= Wire.read(); //LSB y
}
// Show Values
Serial.print("X Value: ");
Serial.println(x);
Serial.print("Y Value: ");
Serial.println(y);
Serial.print("Z Value: ");
Serial.println(z);
Serial.println();
delay(500);
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor and you should see something like this
X Value: 65463
Y Value: 65436
Z Value: 101
X Value: 38
Y Value: 65407
Z Value: 89
X Value: 65509
Y Value: 65455
Z Value: 135
X Value: 65459
Y Value: 4
Z Value: 106
X Value: 65427
Y Value: 65496
Z Value: 94


